講座摘要
葛墨林院士 南開大學陳省身數學研究所 從電磁斗蓬談起 強調電磁波在複雜介質中傳播理論的重要性,以電磁斗蓬(Electromagnetic Cloaking)為例,介紹從簡單介質的折射到非均勻介質電磁張量的廣義相對論描述形式,以及由此引伸出來的一系列結果,可以看到物理學的一些最基本的結論,在科學技術創新中也具有重要的潛在應用背景。本報告還將提及壓縮傳感(Compressive Sensing,CS)和矩陣填充(Matrix Completion)理論,包括它們在圖像處理等相關領域的應用中取得的最新成果。
|
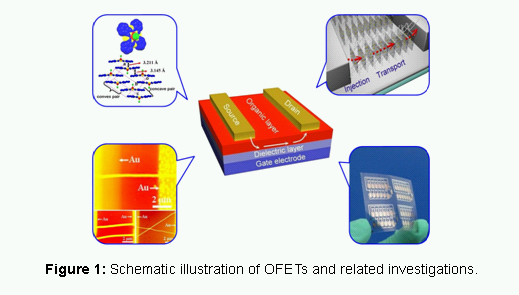
朱道本院士 中國科學院化學研究所、學部主席團成員 Development of Organic Field-Effect Transistors (OFETs): Opportunity and Challenge In virtue of great achievements in the past two decades, organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) have been successfully demonstrated in various area such as electronic papers, sensors and radio frequency identification cards etc. However, there is still a long way to go for realizing the benefits of organic electronics because both opportunities and challenges exist in the further development of OFETs. In this presentation, systemic studies have been performed to meet the urgent requirements of OFETs including the development of material categories, exploration of semiconductor design strategies, fabrication of micro/nano single crystal devices, and investigation of device interface engineering.1-3 Device integration, mainly on solution-processed circuits with low-cost, are also involved.
[1] Di, C. A.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y. Q.; Zhu, D. B. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1573-1583.
|
程津培院士 科學技術部、學部科學道德建設委員會委員 離子液體中的物理有機化學:pKa標度的建立及應用 The room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) are known to promise many chemical processes under environmentally benign conditions. The most contrasting feature of this neoteric green system to the conventional molecular solvents is that they consist of only ions of opposite charge in structure. How would this core character alter the behaviors of the solutes in RTILs still remains very blurred by far, especially on a quantitative basis. And this stimulated the present study on the acidities of carbon acids in RTILs. Equilibrium acidity, i.e. the pKa, is commonly used to describe the trend of a R-H bond to undergo acidic bond dissociation in solution. It is also known as the most widely used physical organic parameter for analyzing various properties and chemical transformations associated to heterolytic bond breaking and bond formation of organic compounds. In the past over a hundred years’ history of chemistry, equilibrium acidity studies have played a central role in the development of modern organic chemistry and several well known pKa scales were established. The dramatic differences found between the pKa’s measured in water and in organic media like DMSO indicate the necessity of systematic pKa studies in ionic liquids. Thus the present work is expected to serve as a quantitative base for analyzing various properties related to heterolytic processes in ILs. The first pKa scales of a series of carbon acids including both aromatic (e.g. 9-substituted fluorences) and aliphatic (e.g. EWG-substituted methanes) molecules in imidazolium-based RTILs with varied chain lengths and counter ions were established under standard conditions. The experimental method was adopted from the Overlapping Indicator Method used for the pKa’s in DMSO. The found structural effects of both the imidazolium moiety and the counter anions on the carbon acid acidities will be analyzed. The RTIL pKa’s are compared with those measured in DMSO and the trend of the variation is discussed.
|
洪茂椿院士 中國科學院福建物質結構研究所 全固態激光技術及其應用 激光技術與原子能、半導體及計算機並稱為二十世紀的四項重大發明。40多年來,激光技術得到了迅速的發展,現已廣泛用於工業生產、通訊、信息處理、醫療衛生、軍事、文化教育以及科學研究等各個領域,進入高速發展期,並將成為21世紀的支柱產業。 我所在激光晶體材料與器件、系統集成和應用等方面已取得了一批成果,並得到規模化工業應用,在作為全固態激光器基礎的人工晶體材料,尤其是在非線性光學晶體研究領域保持著國際領先地位。目前國際市場上的非線性光學晶體產品由我所佔據主導地位。在激光晶體方面也取得了重大進展:國家重點工程使用的許多激光材料可以自主研製,摻釹釔鋁石鎦石(Nd:YAG)、摻釹鎵石鎦石(Nd:GGG)和摻釹釩酸釔(Nd:YVO4)晶體主要技術指標達到國際先進水準,激光晶體出口數量佔國際市場的三分之一,Nd:YVO4晶體佔據了一半左右的國際市場。目前我們針對激光器的需求,研究開發性能穩定、品質可靠的晶體,並且通過激光器的光束質量及實際應用效果來完善晶體質量,保證晶體材料的可靠性、一致性和長期工作穩定性,從而將我國的晶體技術優勢轉化為產業優勢,為全固態激光器的發展起到技術支撐作用。
|
柴之芳院士 中國科學院高能物理研究所、中國科學院化學部 Nuclear Energy Chemistry and Social Development Nuclear energy chemistry refers to the chemical discipline relevant to nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, nuclear decay, and any nuclear-generated energy. Here only the chemistry based on nuclear fission will be dealt with. Nowadays, China is facing the shortage of energy and the press of low carbon emission. It turns out to be that nuclear fission energy is being effectively developed with high safety, because it is a clean, green and environmentally-friendly base energy source. For the sustainable development of nuclear fission energy, a numerous issues of chemistry should be studied, including extraction and purification of nuclear raw materials, composition and fabrication of nuclear fuel assembly, reprocessing and treatment of spent nuclear fuel, partitioning and transmutation of minor actinides and long-liven fission products, and final geological disposal of radioactive wastes, etc. For tackling all these issues, the fundamental chemical research is mandatory, including actinides solid chemistry, coordination chemistry and computational chemistry, separation, partitioning and transmutation of uranium, neptunium, plutonium, and heat-emitting radioactive elements cesium and strontium, and long-lived fission products, like iodine and technetium, etc. In this lecture the present status and future perspectives of advanced nuclear energy chemistry will be selectively addressed with the emphasis on the Chinese progress and roadmap.
|
陶澍院士 北京大學城市與環境學院、中國科學院地學部 Emission, Fate and Respiration Exposure Risk of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in China Emission of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) listed as USEPA priority pollutants from major sources in China were compiled. Geographical distribution and temporal change of the PAH emission, as well as emission profiles are discussed. It was estimated that the total quantity of 16 PAHs emitted from China was 116,000 tons in 2003, more than half of which was from biomass burning. Although vehicular emission contributed to a relatively small percentage of the total emission, it was one of the major sources in urban areas. The emission profile featured a relatively higher portion of high molecular weight (HMW) species with carcinogenic potential due to large contributions of domestic coal and coking industry. The emission increased continuously for four decades starting from 1950 but fluctuated since 1990 due to variation in the production of small-scale coke ovens. A potential receptor influence function (PRIF) model, based on air mass forward trajectory calculations, was applied to simulate the atmospheric transport and outflow of PAHs emitted from China. With a ten day atmospheric transport time, most neighboring countries and regions, as well as remote regions, were influenced by PAH emissions from China. Of the total annual PAH emission of 116 Gg, 93% remained within the boundary of mainland China. Of the PAH outflow from China (8092 tons or 7.1% of the total annual PAH emission), approximately 69.9% (5655 tons) reached no further than the offshore environment of mainland China and the South China Sea. Interannual variation in the eastward PAH outflow was positively correlated to cold episodes of El Nino/Southern Oscillation. However, trans-Pacific atmospheric transport of PAHs from China was correlated to Pacific North America index (PNA) which is associated with the strength and position of westerly winds. An Euler atmospheric transport model CanMETOP was modified and applied to model the atmospheric transport and multimedia fate of PAHs in China based on the emission inventory. The model results were validated by the field observations for concentration levels in atmosphere and soil. The results showed that the spatial distributions of PAHs levels in atmosphere are greatly controlled by emission and meteorological conditions. Elevated concentration levels in both atmosphere and soil were observed in Shanxi, Guizhou, North China Plain, and Sichuan Basin. Significant seasonal variation was found for the transport pattern of PAHs in China with greatly elevated transport flux in winter. The model calculated ambient PAH concentrations were used to evaluate lung cancer risk for the Chinese population due to inhalation exposure to PAHs. The uncertainties of the transport model, exposure and risk analysis were assessed using Monte Carlo simulation, taking into consideration the variation in PAH emission, aerosol and OH radical concentrations, dry deposition, respiration rate and genetic susceptibility. The average benzo[a]pyrene equivalent concentration (BaPeq) was 2.43 (1.29~4.50 as interquartile range, IR) ng/m3. The population-weighted BaPeq was 7.64 (IR, 4.05~14.1) ng/m3 because of the spatial overlap of the emissions and population density. It was estimated that 5.8% (IR, 2.0~11%) of China’s land area, where 30% (IR, 17~43%) of the population lives, exceeded the national ambient BaPeq standard of 10 ng/m3. Taking into consideration the variation in exposure concentration, respiration rate and susceptibility, the overall population attributable fraction (PAF) for lung cancer due to inhalation exposure to PAHs was 1.6% (IR, 0.91~2.6%), corresponding to an excess annual lung cancer incidence rate of 0.65x10-5. While the spatial variability was high, the lung cancer risk in eastern China was higher than in western China and populations in major cities had a higher risk of lung cancer than rural areas. |