Immune Laboratory
Allergic disease: Pentaherbs formula in atopic dermatitis treatment
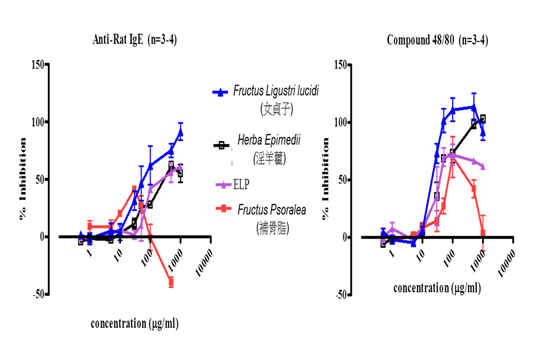
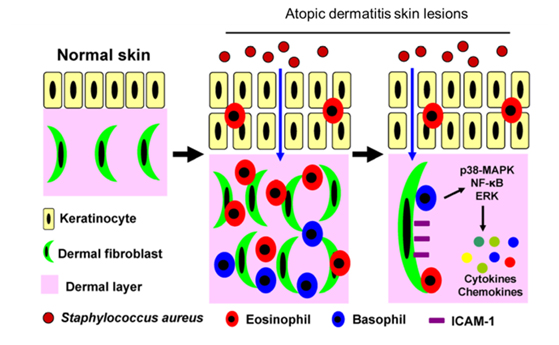
Pentaherbs formula (PHF), consisting of five traditional Chinese herbal medicines, namely Flos Lonicerae, Herba Menthae, Cortex Phellodendri, Cortex Moutan and Rhizoma Atractylodis, is efficacious in improving the quality of life and reducing topical corticosteroid in our clinical and animal studies for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD).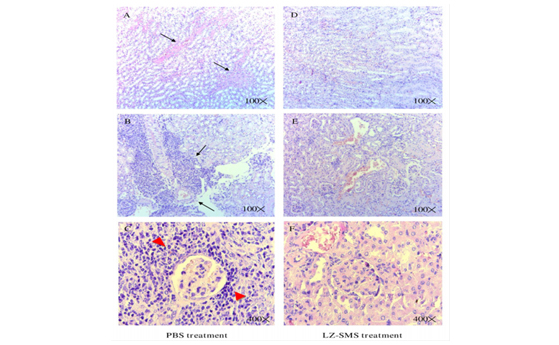
Autoimmune disease: Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi) and Liang Miao San / San-Miao-San supplements (SMS) for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
Sinomenine, an alkaloid isolated from the root of Sinomenium acutum, has been used to alleviate the symptoms of rheumatic diseases. Liang Miao San (LMS), composed of the herbs Rhizoma Atractylodis (Cangzhu) and Cotex Phellodendri (Huangbai), is another traditional Chinese medicine formula for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. By using human primary fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) from RA patients and normal control subjects, we have identified the differential anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine and LMS through the suppression of TNF- -activated FLS by modulating distinct intracellular signaling pathways in RA.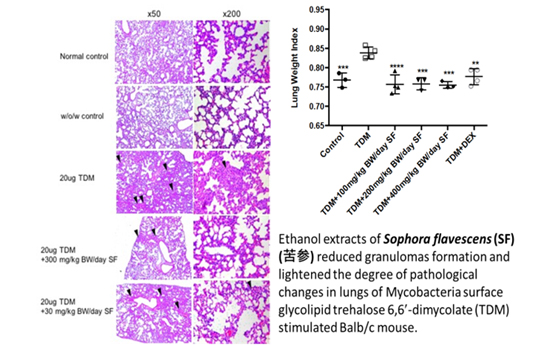
Infection: immunomodulatory activities of herbal medicine in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Tuberculosis (TB) treatment
Pheophorbide a (Pa) has been proposed to be a potential photosensitizer for the photodynamic therapy of human cancer. However, the immunomodulatory effect of Pa, in the absence of irradiation, has not yet been investigated. In collaboration with Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) in France with antibacterial studies, Pa has been shown to possess immunostimulating effect on a murine macrophages cell line RAW 264.7. Pa could significantly stimulate the growth of RAW 264.7 cells.